Installing Objective-C SDK for Data Storage and Instant Messaging
Installing SDK
There are several ways for you to install our SDK and the most convenient one is to use a package manager.
Installing with Package Manager
The easiest way to integrate our SDK into your project is to use CocoaPods.
Make sure you already have the latest version of pod on your computer. If not, please check out the INSTALL section on CocoaPods’ website.
Then, run the following command under the root directory of your project to generate the Podfile:
$ pod init
Following the GET STARTED section on CocoaPods’ website, add the following pod dependency into the target of the Podfile:
pod 'LeanCloudObjc' # A module for all the services
LeanCloudObjc contains multiple Subspecs. You can choose to only add the ones you need:
pod 'LeanCloudObjc/Foundation' # Basic services including Data Storage, SMS, Push Notification, and Cloud Engine
pod 'LeanCloudObjc/Realtime' # Instant Messaging and LiveQuery
The last step is to run the following command to integrate the latest SDK:
$ pod update
You can also run:
$ pod install --repo-update
After installing the SDK, you can open your project with <PROJECT_NAME>.xcworkspace under the root directory of your project.
Installing Manually
First of all, download the latest source code of the SDK.
Then drag and drop the AVOS/AVOS.xcodeproj project file into the project as a subproject:
Now connect the dependencies by going to xcodeproj > target > general > frameworks and adding the following content:
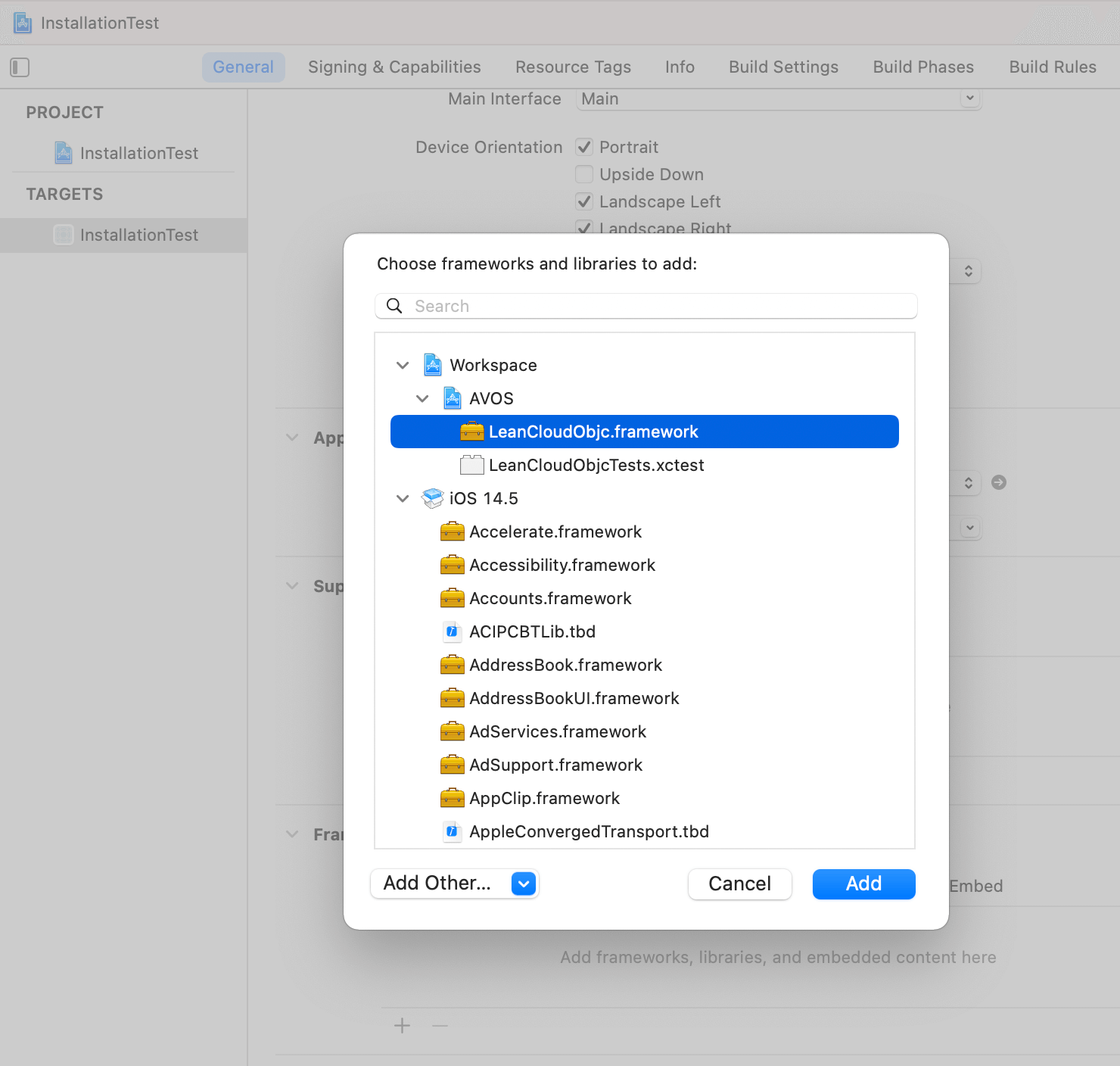
That’s it. You are now ready to use our SDK in your project.
Initializing Your Project
Import the basic modules into AppDelegate:
#import <LeanCloudObjc/Foundation.h>
Then configure the App ID, App Key, and the server URL under the application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: method:
[LCApplication setApplicationId:@"your-client-id"
clientKey:@"your-client-token"
serverURLString:@"https://your_server_url"];
Before using the APIs provided by the SDK, make sure you have initialized your application with the App ID, App Key, and server URL.
Credentials
You can view the credentials of your app by going to Developer Center > Your game > Game Services > Configuration:
- Client ID, also called
App ID, will be used when you initialize the SDK. - Client Token, also called
App Key, will be used when you initialize the SDK on the client side. - Server Secret, also called
Master Key, will be used when you interact with admin interfaces on trusted environments including your own server and Cloud Engine. When you use it, all the permission checks will be skipped. Make sure to keep it private and never use it in the code for the client.
See Domain for setting up the domain.
Domain
To use TDS cloud services, you must bind a custom API domain to isolate your game’s gateway from other developers’. This will help your app avoid being affected by other apps in case of a DDoS attack.
If you plan to use the file service provided by the Data Storage service, which includes the storage of the files carried by multimedia messages sent through the Instant Messaging service (such as images, audios, and videos), you must bind a file access domain.
Binding an API Domain
To bind an API domain, you must first have a domain that already got an ICP license.
See how to bind an API domain
Assuming your domain is example.com, the following steps show how you can bind it to your app as an API domain:
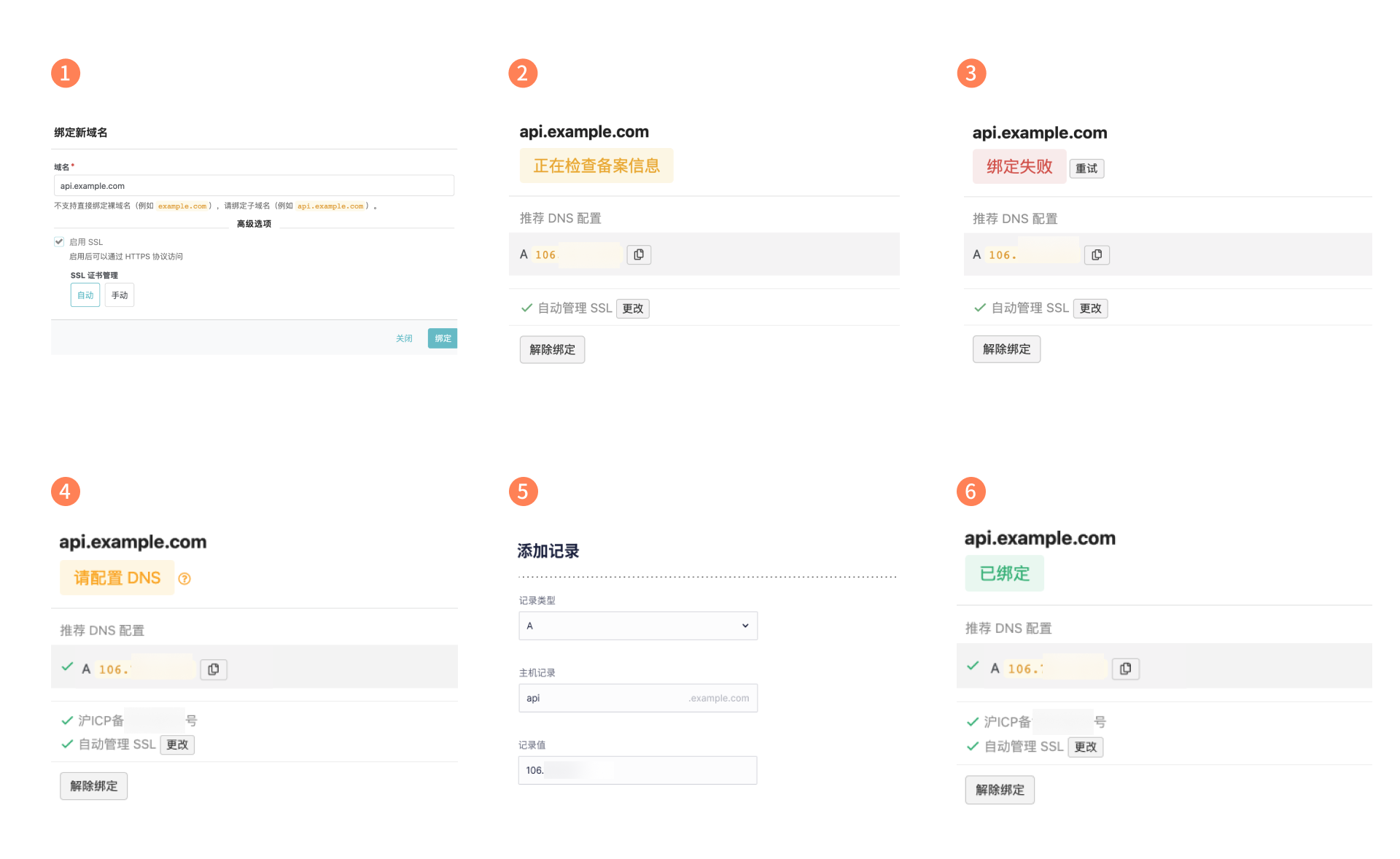
- Go to Developer Center > Your Game > Game Services > Configuration > Domain, then tap Add domain. API domains do not support the direct binding of bare domains. You must add a custom name before the primary domain. In other words, you must create a subdomain, such as
api.example.com. - When the console displays Verifying ICP, please wait patiently.
- If the domain does not have an ICP license, you will see Failed.
- If the domain passes the verification, you will see Configure DNS below the domain.
- Now proceed to the domain service provider’s console, open the domain’s DNS settings, and add an A record (this can direct the domain to an IP address). Copy the custom domain you entered in the Developer Center and the A record displayed under Recommended DNS Configuration into the corresponding fields.
- It will take some time for your DNS records to take effect and for our server to apply for certificates for your domain (if you enabled automatic certificate management), so please wait patiently. Once the record is in effect, the console will display Bound.
When initializing the SDK, please set server_url to the custom domain (e.g. https://api.example.com). The domain shown here is just an example and you should replace api.example.com with your own domain. Please make sure to include https:// in the value of server_url.
It will take some time for you to finish setting up a custom domain. Therefore, TDS provides you with shared domains for testing. However, the availability of these domains cannot be guaranteed and the domains may be prone to DDoS attacks. Before a game goes online, be sure to confirm that the API access domain used for the game is your own domain. Do not use shared domains in a production environment.
Binding File Access URL
Go to Developer Center > Your Game > Game Services > Cloud Services > Data Storage > Files > Settings > File access domain to bind file domains. The process is the same as that for binding custom API domains, except that:
- API domains use A records while file domains use CNAME records. File domains also do not support the binding of bare domains. For example, if your primary domain is
example.com, you can bindfiles.example.comas a file domain. - Once the binding is complete, you must go to Files > Settings > File access URL and click “Edit” to switch to your custom domain.
Each subdomain may only be bound to one game. Additionally, custom API domains and file domains cannot share the same subdomain. If you have already bound a subdomain with a game, you will see “This domain is already bound to an application” when you try to bind it with another game. When this occurs, you may try a different subdomain under the same primary domain to proceed with the binding.
Enabling Debug Logs
You can easily trace the problems in your project by turning debug logs on during the development phase. Once enabled, details of every request made by the SDK along with errors will be output to your IDE, your browser console, or your Cloud Engine instances’ logs.
// Run before initializing the Application
[LCApplication setAllLogsEnabled:true];
Make sure debug logs are turned off before your app is published. Failure to do so may lead to the exposure of sensitive data.
Verifying
First of all, make sure you are able to connect to the server from your computer. You can test it by running the following command:
curl "https://{{host}}/1.1/date"
{{host}} is the custom API domain.
If everything goes well, it will return the current date:
{ "__type": "Date", "iso": "2020-10-12T06:46:56.000Z" }
Now let’s try saving an object to the cloud. Add the following code into the viewDidLoad method or any other method that will be called when the app starts:
LCObject *testObject = [LCObject objectWithClassName:@"TestObject"];
[testObject setObject:@"Hello world!" forKey:@"words"];
[testObject save];
Hit Run to start debugging. This can be done in either a host or a virtual machine.
Then go to Developer Center > Your game > Game Services > Cloud Services > Data Storage > Data > TestObject. If you see a row with its words column being Hello world!, it means that you have correctly installed the SDK.
See Debugging if you’re not seeing the content.
Debugging
This guide is written for the latest version of our SDK. If you encounter any errors, please first make sure you have the latest version installed.
401 Unauthorized
If you get a 401 error or see the following content in network logs:
{
"code": 401,
"error": "Unauthorized."
}
It means that the App ID or App Key might be incorrect or don’t match. If you have multiple apps, you might have used the App ID of one app with the App Key of another one, which will lead to such an error.
The Client Cannot Access the Internet
Make sure you have granted the required permissions to your mobile app.